Aerodynamic lift? Explain rather with ice-floe
than Bernoulli!
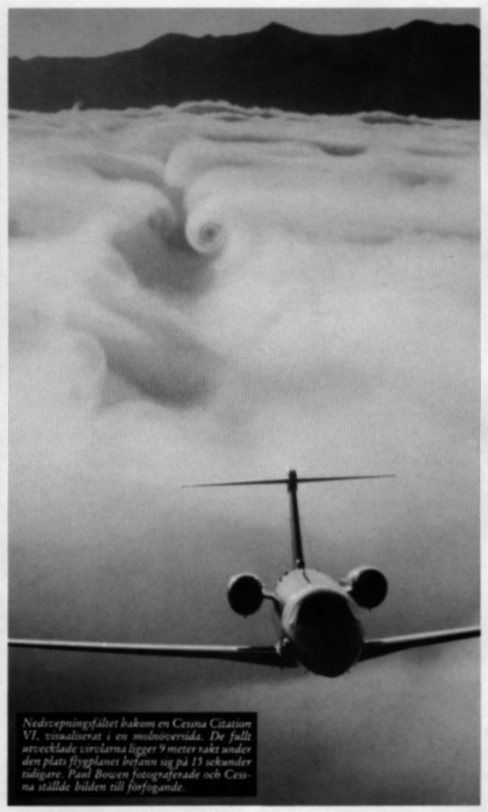

The
downwash sheet behind a Cessna Citation VI, visualized in a cloud upper side.
The fully developed whirls lies 9 metres straight under the location the
aeroplane was 15 seconds earlier. Paul Bowen photographed and Cessna made the
image available.

There is
one clear similarity between to fly and to "jump" from ice-floe to
ice-floe. The jumper can only hold oneself up by accelerates new ice and water
masses downwards all the time. An illustration by Torgil Rosenberg.
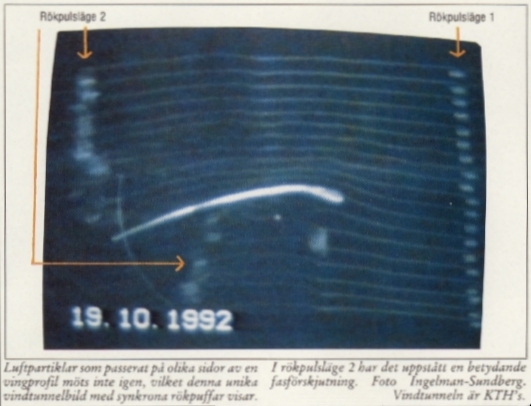
Air particles that have passed on different sides of an airfoil, meets not again, which this unique wind tunnel picture with synchronously air puffs shows. In air puff situation two, it had arisen an important phase shift. Photo: Ingelman-Sundberg. The wind tunnel is KTH´s.
Pilots
comes never to understand how dangerous "the surges" after big
aeroplane is, as long as they not know how aerodynamic lift really is created.
by Martin Ingelman-Sundberg
Goebbels: If a lie repeats enough many times it become raised to truth.
Millions of pilots live on a lie in a literal sense. In the flying school they
have been teached that the wing is lifting in order to the air speed
acceleration on the upper side of the airfoil, is creating under pressure. Such
description is in opposition against fundamental physical laws. The true is
that the pressure changes, that gives lift, comes from inertial forces in the
air mass that influence by the wing through the road forth. Compare gladly with
to go forward to somebody on water jumping on ice-floe.
The usual description could possibly be looked at like a harmless apparent
simplification, until it began to come alarming reports about surges after big
airliner. Today it is an international scandal that the authorities continue to
provide aviation theory that builds on a misinterpretation of Bernoulli's law.
Why shall pilots learn aviation theory?
All children teach oneself through accumulative practical experience by oneself
to walk, without to know a drizzle about balance, center of gravity, inertia
mm. It works fairly well. They maybe slip and fall on ice-coated road on the
winter and hurt one a little, but they teaches one successively what makes
hurt. None help instruction from outside is needed. It maybe exists now in ours
genes. Similar is it for adults that want to skate on a wash rink on ground.
They only risk hurting oneself.
It becomes entirely different for the one who want to broaden the skating
within the range of possibility, on lake ice. Then can it, the very first
contact with weak ice and cool water, result in that the new experience
nevermore need to make use of. Instead it is practical to, via
"theory", learn where the lethal limits go.
That pilots should understand how their aircraft wings works, have a similar
motivation.
The purpose with theory teaching for pilots is to give them a knowledge with
whose help they, for unexpected and never trained situations, shall be able to
act on best manner. The condition is that there has been a correct physically
teaching. Otherwise the teaching is meaningless.
Reaction forces
Right up to the middle of 1930 century described flight people the aerodynamic
lift on an overall and physical correct way, with that the wings accelerates
air mass downward, at which the reaction against the airs inertia gave the aerodynamic
lift. The faulty Bernoulli-interpretation began also come with, but got not
stand alone, as today. That the wing "puff at" (= start the movement
downward of) gradually new air mass was the brothers Wright also aware of.
Lilienthal had 1895 in detail described how under and over pressure around the
airfoil occurs through centrifugal forces on the air mass elements, which by
the wing is forcing to move oneself in a bend courses. Centrifugal force have
people easy to understand and the fact is that this description equals, despite
the simplicity, excellent in our times modern calculations, that has done by
the super computers.
In a little more scientific terms it can be sum up as follows: Local pressure
change initiates by a body's fixed surface and this surface force passing
sluggish air particles to change its momentary movement direction. From that
initialized pressure change affects secondarily also the local speed along the
movement path, after which in third hand the pressure change reinforces because
of increased centrifugal forces at the same path radius.
This interaction is also the reason for that the decrease of pressure above a
lifting profile, because of the higher speed, will become absolutely seen
bigger than the increase of pressure under a lifting profile, there of course
the speed decreased because of there existing a higher pressure.
In spite of the fact that the pioneer thus could describe the principle airlift
creation physically correct, so could they yet not calculate the pressures size
and distribution between the wings over and under side. This became the root to
future misunderstanding.
Daniel Bernoulli (1700-1782), professor in math and medication, published 1738
in his book "Hydrodynamica" among other things fundamental experiment
and conclusions about relation between pressure and kinetic energy for water
that streamed out of hole in vertical channels. Since the kinetic energy is a
function of both the mass and the speed gives this also a relation between the
pressure and the speed.
Mathematically trick caused the aviation's life lie
Leonard von Euler (1707-1783) mathematician and friend with Bernoulli, set up
fundamental equations for how a fluid ought to flow around a body, at which he
start from the balance between inertial forces and pressure forces on each
separate small fluid element. Euler's equations were however under two
century's impossible to solve and make use of, besides in an important special
case: "an non compressible fluid mass elements movement along a straight
line". The relation between kinetic energy per volume unit and locally
pressure that Euler got from this special case, corresponded to it that
Bernoulli studied, why von Euler say have given it the name "Bernoulli's
equation". Bernoulli self compare also the waters movements with a, during
the force of gravity's influence, freely falling body.
Bernoulli self have never written "that acceleration causes pressure
reduction", that is said in the pilot education -- the air traffics
supervision authorities prescribe for the pilot education. On the contrary he
have directly pointed out that this is unsuitable to say, while "that
pressure reduction causes speed acceleration" is acceptably to say.
Through to introduce the simplifying condition "absolutely incompressible"
you could treat the entire flow field with an arithmetic technique with a pure
so called velocity potential. This technique builds on certain mathematical
"tools" as sources, sinks and whirls (circulation) which only
simulates induced velocities. The technique makes it possible that if you
beforehand on experimental behalf, established the outflow direction from the
wing trailing edge so could you calculate the local speeds in the entire field
around the wing. This even without computers.
Then the velocity field has been calculated, made possible a diagnostic
"reversed" utilization of the Bernoulli equation, determination of
what the pressure must be in present point in order to the fluids inertia mass
there shall have reached the predictated velocity. The early theorists
consciousness about the reversed Bernoulli use seems, however later, have been
forgotten also among many Professor's of flow.
This, the final stage itself in the potential theory calculations, is what who
has been giving the cause of the entire aviation worlds, included ICAO,
unfortunate misunderstanding about that Bernoulli's law would say "that
acceleration causes pressure lowering" and who come to twist all
education. Then the defective fundamental statement have combine with a whole
serial physically entirely wrong example in order to point out the statements
rightness. And on the top of this equally defective argument and example on why
the velocity shall become high, so that the defective statement can be apply.
Like this aeroplane creates its aerodynamic lift
On the cover to FLYING, March 1992, it showed a photo that can replace many
hours aviation theory. It can say visualize the actual fundamental principle
for flying according to system heavier than air. And it does it not in a small
wind tunnel but up in the real aviation environment. The image ought to have
its location in the theory hall in every aviation school.
A Cessna Citation coming climbing up out of the cloud above Lake Tahoe in
California. In the tail turret to an old B-25 Mitchell, who is flying 500 metre
in front of, be seated the photographer Paul Bowen. Also when the Cessna come
entirely above the cloud so force it the air downwards, so that the cloud upper
side becomes first bath tub - formed, in order to 15 seconds after the passage
have roll up to two concentrated whirls, which move oneself downwards with a
constant mutual distances.
Continuously take-off from successively new masses of air
In order to hold the aeroplane in the air, against the Earth's gravity, must
the aero planes wings continuously accelerate a certain part of the air, that
pass by, in opposite direction, i.e. downwards, so that this air, then the wing
just passed, has got an certain velocity downwards.
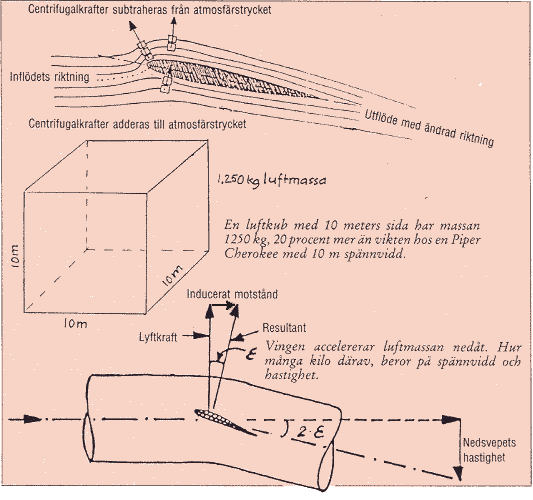
That air have mass (measures in kg). One cube air with same side as the span on
a typically sport aeroplane contains 1250 kg air mass at ground pressure. One
thought air cylinder with Cessna Citations span both as diameter and length
contains, on the altitude 6000 feet, a mass of not less than 3,5 tone (!) and
it have furthermore an accordingly inertia. The inertia does that the air mass
not changes voluntarily its initial rest condition when the wings
"attack" force it to move oneself away downwards. This corresponds to
the so-called Newton's First Law. The air come therefore, according to Newton's
Third Law, to exercise precise equally big reaction force against the wing
(i.e. aerodynamic force) as require for its mass contents successively
acceleration downwards.
This happens through that it arise a reduction of the airs pressure towards the
wings upper side, whose limitation surface, of course, "ran away"
downwards from the stationary atmospheric air. Some of the atmospheric pressure
balances then by the inertial forces that must overcome in order to give the
air velocity downwards in direction towards the surface, which means that they
subtracts from the pressure towards the surface. The wings underside
"force one's way" downwards, why the inertial forces is added so that
the pressure against this get increased. As result arise that pressure
different between the upper and under sides that gives the actual aerodynamic
lift.
Each second you can say that the Citation wing "takes take-off from"
(=activates) so much air that holds in a cylinder with the same diameter as the
aero planes span and with the length = that distance as the aeroplane transport
oneself during a second. However, the take-off goes on successively during the
wing passage.
The size on this "equivalent activated mass" come to light already
for 75 year ago as a results of a detailed calculation which professor Ludvig
Prandtl did as soon he designed his so-called vortex theory for wing
calculation. If the wings aerodynamic lift distribution in span width line
differs from that at optimally stated, so correspond it that the activated mass
(the cross-section of it) becomes some reduced, which gives increased
"lift" resistance. The relation is valid unchanged today and the
vortex theory is still the most used method of calculation.
There is one direct similarity also with to jump on ice-floe, there you take
take-off from successively new ice and water masses which accelerates downward.
It is also the same principle that being used when one, through to angle out a
rudder at an trailing edge, gives the air mass an additional acceleration
upwards or downwards exactly before it leaves the wing.
The surge movement
Immediately when the wing passed so has earlier mentioned air mass left of with
a certain speed downwards. The kinetic energy, that has been supplied, recycles
never more. This loss of energy is the reason for the so-called (lift)induced
resistance. It will not at all be about any little local around current from
pressure to suction side around the wing tip itself, as it usually says. If it
shall be called "leakage" so happens it both far above, under and
outside the tips.
The expression that the leakage causes the induced resistance comes from a
comparison with an imaginary infinite long airfoil. This would, you see, not
need cause any remaining downwards velocity, why the lift-induced resistance
would become zero. Here shall we not become absorbed in this, or how the wings
profile in detail works. Just establish that the physical important phenomenon
for the airfoils function is that the undersides current of air not be able to
follow the surface around the trailing edge but release from the surface,
simultaneous as the current round the leading edge and above lie close and
remains there.
In the Citation case in point (span 15,9 m, weight 6700 kg, speed 175 knot/87
m/s) the wing is passing each second through a cylinder containing 18,4 tone
air. The inertial mass at all this air is given successively a down speed of
3,7 m/s.
Nearest behind the plane one can see that the cloud upper side principally
forced away downwards. Further back, i.e. a certain time after the passage,
have another air from the sides reached to flow in above the initially down
washed air and also have the air below forced out to the sides. Gradually have
the two anti rotated whirls formed. Theirs whirl center stabilizes on a mutual
distances of 79 percent of the wings span (Prandtl). Theirs distance in the
picture is therefore 12,6 m, which can make use of to give a length scale in
this cross-section.
It can be calculated that the whirl center on the picture lies about 9 metre
under that height there the wing really passed then the wing initiated the airs
movement downwards. Compare gladly the development of the whirls in the surface
of water after a paddle stroke, it is the same thing.
For wings with a large extent in lengthways relatively the span, for example
Draken and Viggen, arrive in time those whirls that has been caused by the
wings front parts, often to concentrates already above the wings own back
parts.
How long live they?
With lead of the aero planes weight, span and speed and with current air
density, it will work to calculate the whirls strength and thus that periphery
velocity as exist on different radius from center. It is in this case 15,4 m/s
0,5 m from the whirls center.
Cessna Citation has fairly low weight per metre span and flying here pretty
fast, why these whirls is relatively harmless. If its speed is reduced to half,
the whirl strength is doubled. A Concorde with the weight 185 tones within 26
meters span, would at now current speed give whirls that is very dangerous for
smaller aeroplane, 17 times so strong as Citation! A 747 - 15 times, DC-9 - 5
times and Piper Cherokee 0,25 times so strong.
Those who - maybe - has experienced the gust when she or he with its Cherokee
in steep turn have crossed their own whirls, can think oneself this gust 60
times stronger. So becomes it to fly into the aerodynamic lift vortices, or the
surge waves, after a slowly flying 747.
In USA even a total loss occurred when a DC-9 during school flying in relation
with the landing, came too close after a 747 and was thrown over on back and
went in the ground.
The time it takes before the whirls has reduced out and transited in unarranged
turbulence, depends on the atmospheres own turbulence. In calm air it last
longest and it can be a question about many minutes before they have reduced in
essential grade. Before the extent of this problem in full realized, reach USA
for 25 year ago, lose its prototype to the supersonic bomb plane B-70, then a
escorted fighter was captured by its whirls and collided with it.
That generally used expression aerodynamic lift vortices gives a deceitful mild
association, even if it is the same thing that are meant.
Martin Ingelman-Sundberg have in four year fought for that aerodynamic
lift shall be describe correct in the theory teaching for pilot. But those in
power who can correct the rules for the design of educational materials and
examination, takes either not his knowledge seriously, or not realize the
seriousness in to continue cheat an entirely pilot collective. It would be
interesting to know which, willingly presented by the flight safety boss who is
enter upon one's duties on the Swedish Civil Aviation Administration.
Ingelman-Sundberg is now retired after 40 year as a professional aerodynamics
of which 30 as boss for the section for slow speed aerodynamic at The
Aeronautical Research Institute of Sweden. He is still flying; with certificate
conquer for 54 year ago.
Newton's laws:
Law l define the conception a mass' inertia, i.e. that if it not
influence by any external force, so preserve it its initial state of motion or
rest.
Law 2 states how big force is required for to change the state, i.e. to
accelerate the mass in any direction. It is also called the general force
equation.
Law 3 saying that if a body A influence a body B with a certain force,
so influence also body B body A with exactly same force.
Bibliography
Magazine
Ingelman-Sundberg, Martin, Lyftkraft? Förklara hellre med
isflak än Bernoulli! MACH 56 (nr 1, 1994), s 43-45.